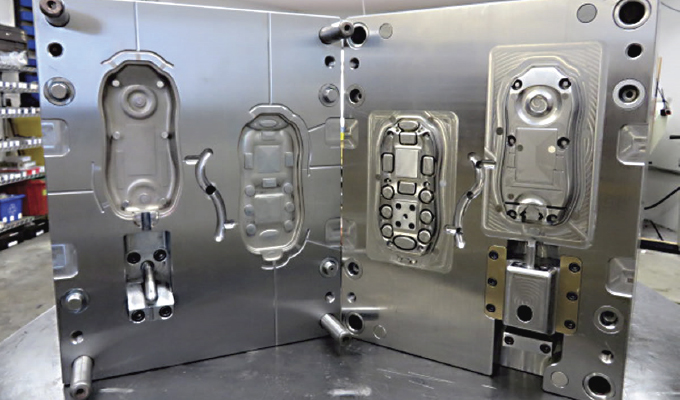
Injection molding is the preferred method for mass-producing precision plastic parts. However, its upfront costs can be hefty. It’s worthwhile to tweak the production process to decrease both the complexity and the overall expense of your project.
- Before diving into some tips, let’s pinpoint the primary cost factors in injection molding:
- Tooling costs, which encompass the design and machining of the mold.
- Material costs, based on the amount of material and its price per kilogram.
- Production costs, tied to how long the injection molding machine runs.
For smaller batches, tooling has the greatest impact, contributing to roughly 50 to 70 percent of the total cost. Therefore, it’s essential to plan in advance to accommodate your project’s needs.
Most molds are CNC machined from metals like aluminum or steel for durability. These molds can cost anywhere from $10,000 to $100,000. If you’re producing thousands of parts, that investment is justified. However, for smaller batches, 3D printed molds have become quite popular owing to improvements in additive manufacturing.
Here are some tips to help you optimize the cost of your injection molding project:
1. STICK TO THE STRAIGHT-PULL MOLD
Using side-action cores and other in-mold mechanisms can bump up tooling costs by 15% to 30%. This means you might face an extra tooling expense ranging from $1,000 to $1,500. To keep your production on budget, avoid using side-action cores and other mechanisms unless absolutely necessary.
2. REDESIGN THE INJECTION MOLDED PART TO AVOID UNDERCUTS
Undercuts add to costs and complicate things, so it’s always worth the effort to get rid of them where possible.
3. MAKE THE INJECTION MOLDED PART SMALLER
Smaller parts can be molded faster resulting in a higher production output, making the cost per part lower. Smaller parts also result in lower material costs and reduce the price of the mold.
4. FIT MULTIPLE PARTS IN ONE MOLD
Using a single mold for multiple parts is standard practice. Typically, you can fit six to eight small identical parts in one mold, cutting down production time by roughly 80 percent. You can also place parts with varying shapes into the same mold, much like model airplane kits. This strategy significantly trims assembly costs.
Sometimes, two assembly parts share the same main body. With a touch of inventive design, you can craft interlock points or hinges at symmetrical spots, essentially creating a mirrored part. This lets you use one mold for both parts, halving your tooling expenses.
5. AVOID SMALL DETAILS
Manufacturing a mold with fine details takes longer due to extended machining and finishing times. Text serves as a prime example, often demanding specialized techniques like electrical discharge machining (EDM), which can drive up costs.
6. USE LOWER-GRADE FINISHES
Hand-applying finishes to molds can be pricey, especially for high-grade finishes. If your part isn’t meant for cosmetic purposes, it’s best to skip the expensive high-grade finish.
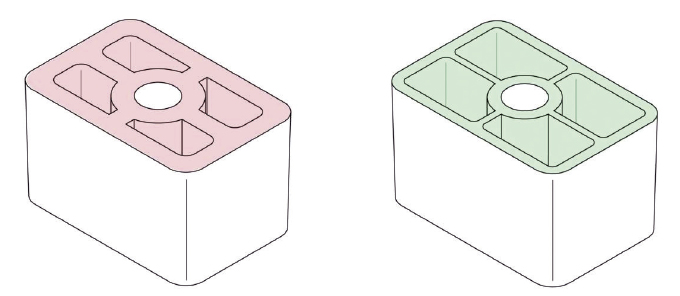
7. MINIMIZE THE PART VOLUME BY REDUCING WALL THICKNESS
Slimming down the wall thickness of your part is a prime strategy to reduce its volume. This not only uses less material but also significantly speeds up the injection molding cycle. For instance, cutting the wall thickness from 3 to 2 millimeters can slash the cycle time by 50 to 75 percent. Why? Thinner walls allow the mold to fill faster.
Even more crucial, thinner parts cool and set more rapidly. Consider that nearly half of the injection molding cycle is dedicated to letting the part solidify, with the machine on standby. However, it’s essential to strike a balance. You don’t want to compromise the part’s rigidity, which could affect its mechanical performance. To maintain stiffness, consider adding ribs in strategic areas.
CLOSING CONCERNS
Also, note that opting for 3D printed molds can drastically reduce mold expenses, bringing them down from thousands to just a few hundred dollars. However, this choice is most suitable for short runs where wear resistance isn’t a primary concern. For high-volume production runs (10,000 to over 100,000 units), material and production costs eclipse the impact of tooling costs on the overall expense. In such scenarios, your focus should be to reduce both the volume of the part and the duration of the molding cycle.
FOR MORE INFORMATION
Protolabs Network, part of Protolabs’ global manufacturing services, specializing in 3D printing, CNC machining, injection molding, and sheet metal fabrication, offering a wide variety of materials and surface finishes. We have some of the broadest capabilities in the industry, so we can accommodate almost any manufacturing request. When parts with intricate geometries or highly cosmetic finishes, there’s a partner in the Protolabs Network that can produce it. For more information, visit www.hubs.com/protolabs-network.
MODERN PUMPING TODAY, February 2024
Did you enjoy this article?
Subscribe to the FREE Digital Edition of Modern Pumping Today Magazine!


