Highly poisonous heavy oil, a waste product of petroleum refineries, is still blown through the funnels of tankers into the air without being filtered. To reduce the burden on the environment, especially near the coast, while being able to react better to price fluctuations, Qatar wants to arrange the future operation of its entire LNG fleet on a flexible basis. The dual-fuel engines that MAN Diesel & Turbo developed for this purpose can optionally be operated with heavy oil or with the liquefied natural gas in the hold. To do this, the boil-off gases are reliquefied under high pressure and injected into the ship’s engine. Since ships are always operating and only brought into dry dock for maintenance once in five years, the high-performance pumps used for this purpose must be extremely robust and temperature-resistant. One of the favorites for the supply of these high-performance pumps is Cryostar SAS, a specialist in cryogenic gases. As a partner of this French manufacturer, Lewa GmbH was entrusted with the development of a new drive unit that meets the strict requirements for this application.
Heavy oil is easily obtained, difficult to burn, and can be fed into the engine at low pressure. When the large transport ships of the Q-flex and Q-max LNG fleet were built nine years ago, the decision was therefore made to use slow-running diesel engines, since these are also thermally more efficient than steam turbines and burn less fuel. But it is foreseeable that tankers like those in Qatar will have to convert to other fuels in the future for environmental reasons—at least near the coast. Transport ships with dual-fuel engines like the ones the Emirate wants to use, however, are new territory for everyone involved. Many ship-owners found the technical risk too high, since LNG can be transported safely in the liquid state only at very low temperatures. However, the option of using on-board natural gas as a fuel is also becoming more attractive because engine efficiency is improved in comparison with heavy oil.

USING BOIL-OFF GASES
The challenge for the ships is that liquefied gas warms up during travel, partly converting back into its gaseous state, meaning that its volume grows by a factor of 600 and the pressure in the storage tanks rises. Venting these boil-off gases harms the environment and reduces the profits of both the producers and the charter companies. Instead, in the Q-flex and Q-max LNG fleet, they are therefore reliquefied. This yielded the idea of making the gas available to operate the ship. Additional equipment will therefore be provided to make the fleet flexible in its choice of fuel. This allows a reaction to the current prices in the specific export country: If gas is trading high there, it’s better to sell it than to burn it in the ships’ engine. But in the opposite case, it pays to operate the ship with LNG. But since the gas is extremely explosive, absolutely tight special equipment is needed that can withstand both the temperatures and the high pressures.

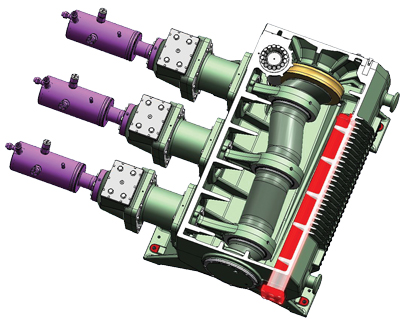
SPECIAL EQUIPMENT: HIGH-PERFORMANCE TRIPLEX DRIVE UNIT
As a researching and productive company, LEWA develops technologies and works out solutions for a wide variety of its customers’ applications. Products are primarily used in the oil and gas industry, in the area of gas odorization, refineries, and petrochemistry, but also in the manufacture of plastics, detergents, and cleaning agents. Additional application areas can be found in chemistry, the cosmetics industry, in pharmaceutical and biotechnology, in the food and beverage sector, and in power supply. LEWA currently has approximately 840 employees and has sixteen subsidiaries worldwide as well as representatives and sales offices in over eighty countries.

With the Triplex pumps that Cryostar and Lewa developed together, both companies are ideally prepared for this new application. The French company is a pioneer in this area and developed the pump heads to meet the requirements for cryogenic liquefied gases. The corresponding G3M triplex drive unit is a special-order production of the Leonberg-headquartered system builder.
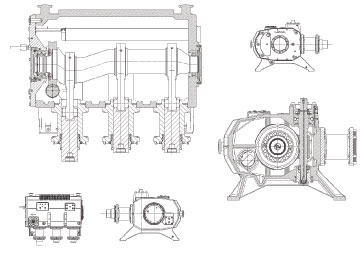
Cryostar has the know-how needed to work with cryogenic gases at temperatures ranging from -256 to -328 degrees Fahrenheit (-160 to -200 degrees Celsius), while Lewa has the robust, low-maintenance drive unit technology needed for long-term operation, which explains the synergy between the two companies. With a rod force of 125 kN, the G3M transforms the rotary movement into an oscillating movement, achieving a maximum power of 160 kW. The development also closes a gap in the manufacturer’s portfolio. This is an intermediate size with a 4.72 inch (120 millimeter) stroke length, and we see additional market potential for it.

The first prototype from Cryostar and Lewa is currently in the testing phase. If the results of these tests and the first trips under load come out positive, the system will be tested on a ship under real conditions. The costs for the retooling are estimated to be about $15 million per ship, with the total order volume for all forty-five ships in the Q-flex and Q-max fleet coming to $700 million. ■
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Thomas Bökenbrink is a product manager for Lewa GmbH, the world’s leading manufacturer of metering and process diaphragm pumps as well as complete metering systems for process technology. The company, headquartered in Leonberg, Germany, has developed over just a few decades into an international group, and its position in the world market was further strengthened by its integration into the Japanese Nikkiso Co. Ltd. in 2009. For more information, visit www.lewa.com.
_________________________________________________________________________
MODERN PUMPING TODAY, February 2014
Did you enjoy this article?
Subscribe to the FREE Digital Edition of Modern Pumping Today Magazine!
![]()


